Screening
Take steps for early detection
What Is Prostate Cancer Screening?
Screening means checking for signs of prostate cancer before symptoms appear.
Because prostate cancer often grows slowly and silently, early screening can make the difference between a simple, curable condition and one that’s discovered too late.
Screening helps detect cancer at its earliest — and most treatable — stage.
For many men, this means living a long, healthy life with peace of mind.

Why Screening Matters
In Pakistan, awareness and regular check-ups are increasing — but many men still avoid talking about prostate health until problems arise.
Early detection through screening:
Saves lives — by finding cancer before it spreads
Offers simpler treatment options with fewer side effects
Improves survival and quality of life
Reduces anxiety — knowing your status brings clarity, not fear
Remember: getting screened doesn’t mean something is wrong — it means you care enough to make sure everything is right.
Screening is not about fear — it’s about freedom, awareness, and peace of mind.
By taking a few minutes for a simple test, you could protect decades of life — for yourself, and for those who love you.
Know your risk. Get screened. Stay strong, stay informed.
💙 Early detection saves lives — and it starts with you.
Types of Prostate Cancer Screening
1. PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) Test
A simple blood test that measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate.
High PSA levels may indicate prostate inflammation, enlargement, or cancer.
Low or stable levels are generally reassuring.
Your doctor may repeat the test over time to track changes.
2. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
A quick and painless physical exam performed by a doctor.
By gently feeling the prostate through the rectum, the doctor checks for:
- Lumps
- Hard areas
- Unusual enlargement
It takes less than a minute and can help detect cancers that the PSA test might miss.
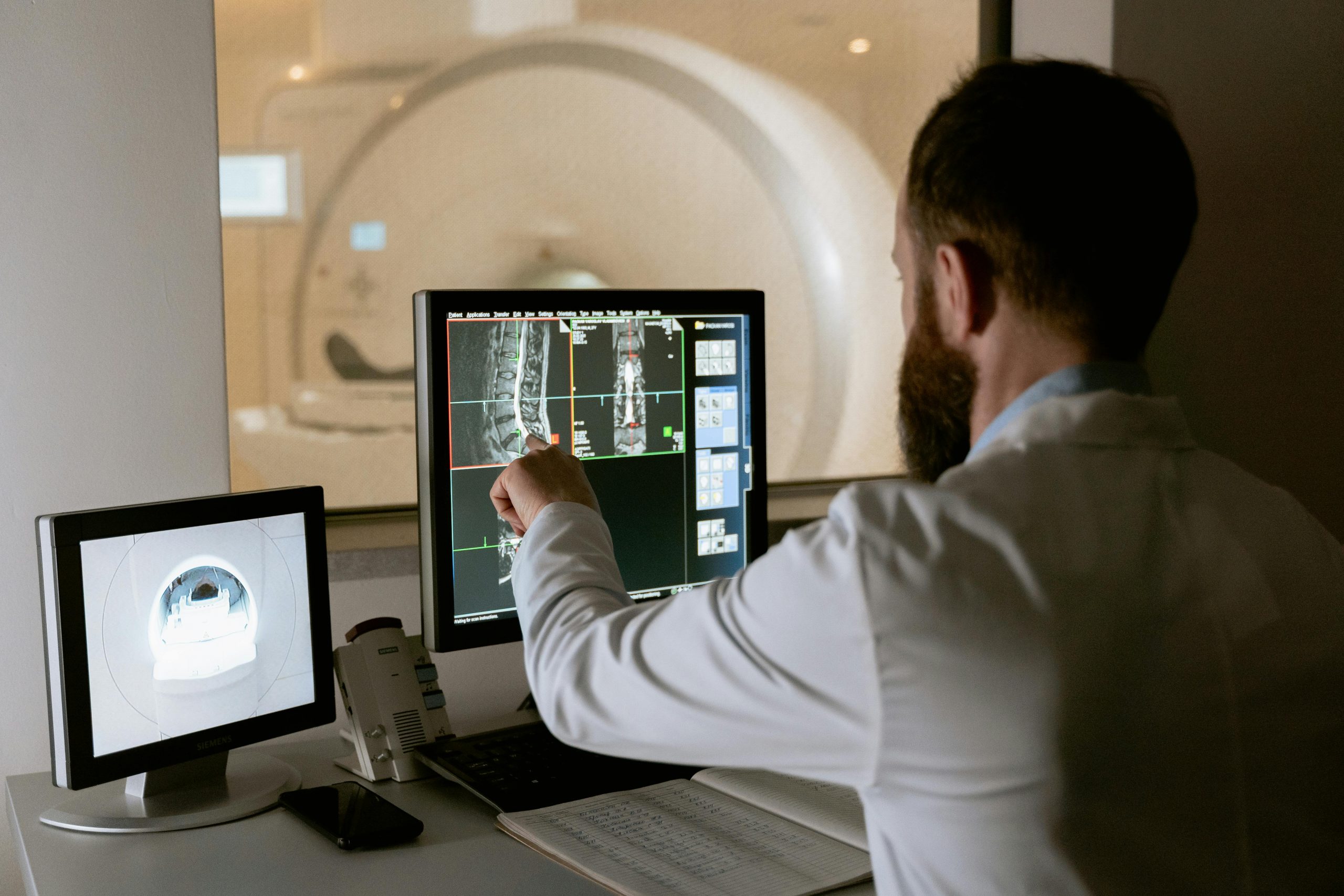
3. Advanced or Follow-Up Tests
If PSA or DRE results show something unusual, your doctor may recommend:
MRI scans or Ultrasound — to visualize the prostate
Biopsy — taking a small tissue sample for testing
These tests confirm whether cancer is present and how advanced it might be.

Who Should Get Screened?
Screening recommendations depend on age, risk factors, and family history.
| Risk Group | Recommended Starting Age | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Average-risk men | Age 50 | Every 1–2 years |
| Men with family history (father, brother, or son with prostate cancer) | Age 40–45 | Every year |
| Men with symptoms (urinary or sexual) | At any age | As advised by doctor |

What to Expect During Screening
The tests are quick, non-invasive, and confidential.
You may be asked to avoid ejaculation or heavy exercise 1–2 days before a PSA test (these can slightly raise PSA levels).
Results are usually available within a few days.
If results are normal, your doctor will simply recommend when to test again.
If results are slightly elevated, further checks are done — it doesn’t automatically mean cancer.
Understanding Your Results
| PSA Level | What It Might Mean |
|---|---|
| Normal (usually below 4 ng/mL) | Low risk of prostate cancer |
| Slightly elevated | May be due to infection, age, or enlargement |
| High | Needs further evaluation, not always cancer |
Roughly 2 out of 3 men with an elevated PSA do not have prostate cancer — but follow-up testing ensures nothing is missed.
What comes next?
✅ If Results Are Normal:
Keep up with regular screenings as advised.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle — exercise, balanced diet, and no smoking.
Stay aware of any new urinary or sexual symptoms.
⚠️ If Results Are Abnormal:
Don’t panic. Abnormal PSA levels can result from many causes.
Follow your doctor’s advice for further tests.
Bring a family member or friend to appointments for support and better understanding.
Stay informed — knowledge reduces fear.

Hope in numbers
Focus on the possible positive outcomes after screening. Screening doesn’t just detect cancer — it helps you make informed decisions about your health long before problems arise.
01.
Early Detection
9 out of 10 men whose prostate cancer is found early through screening live at least 10–15 years or more after diagnosis.
02.
Post Treatment
Over 95% of early-stage prostate cancers are successfully treated or managed.
03.
Stay Aware
Men who start regular screenings in their 40s and 50s often avoid advanced disease entirely.

